Medical Disposable
Disposable Medical Sensor & Circuit Solutions
SSI has been manufacturing disposable medical sensors for more than a decade. In doing so, we have helped pioneer a bevy of effective manufacturing processes for this unique arena. Product development has been extremely active in this exploding medical sensors market, and we are ideally positioned to support the evolution of your disposable medical sensors needs.
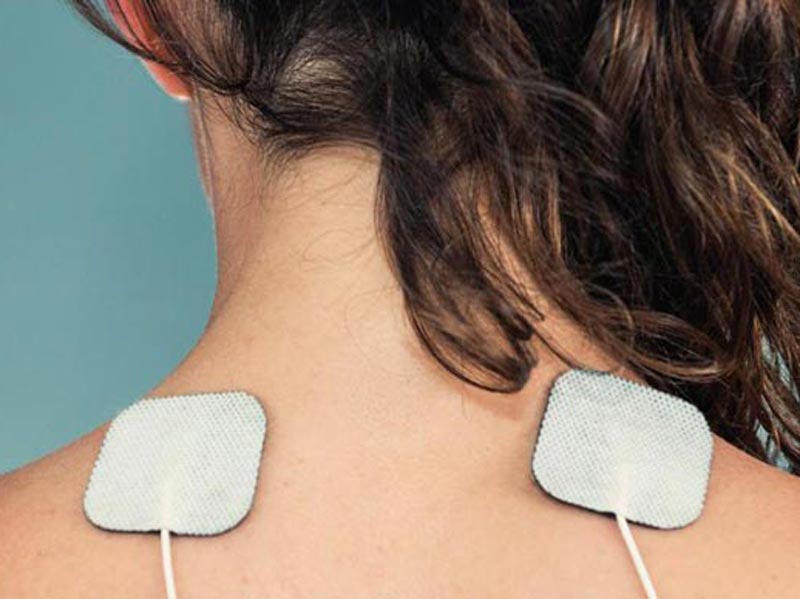
SSI Medical Sensors: Flexibility in Patient Monitoring
One of the key attributes of a disposable medical sensor is its flexibility or ability to conform to the human body. This is key for both good adhesion and also adequate data reporting to its matting electronics package.
Likewise, SSI Electronics has learned to be very flexible in thinking, as no two disposable medical projects are the same. Our engineers must be both open‐minded and confident in design and best practice as we aid in development of these critical class II medical devices.
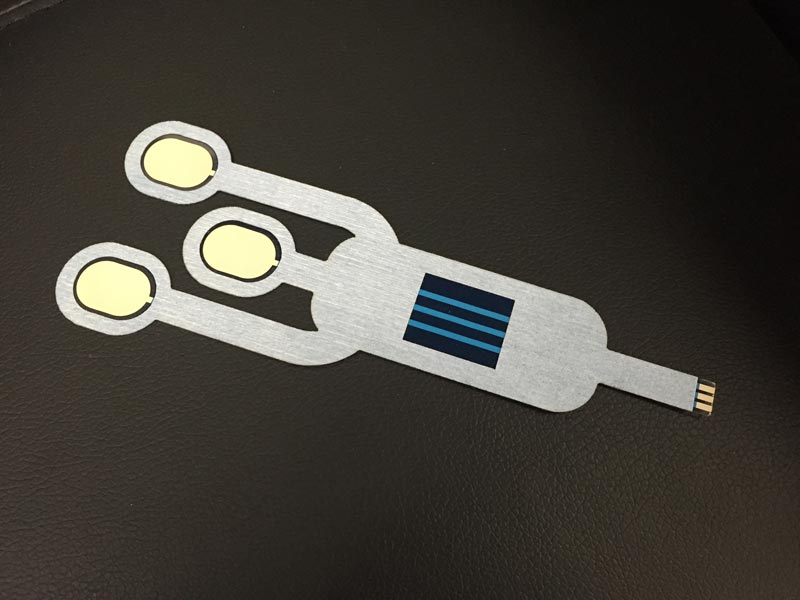
The Anatomy of Disposable Medical Sensors
Medical sensors can be made up of many different components and are generally comprised of: a circuit, patient attachment layer and electronics. The disposable medical sensors must adhere directly to a patient’s skin to function properly. This connection provides an electrical bond, and in some instances, a mechanical bond as well. The circuit, which is made of a thin flexible layer of either polyester or polyimide provides the pathway between the individual and the electronics. The electronics includes the proprietary mechanisms for detecting, monitoring and discerning the various human conditions.
Medical Circuit Attachment Via Hydrogels
Medical sensors are generally attached to the human body by using a gel like substance, referred to as hydrogel or conductive gel. Hydrogels are three-dimensional, hydrophilic, polymeric materials capable of absorbing large amounts of water or biological fluids. Due to their high water content, porosity and soft consistency, they closely simulate natural living tissue. Essentially it is this high water content that makes these sticky substances conductive, providing an electrical pathway between human skin and the medical device. When using hydrogels for disposable medical sensors it is important to keep in mind the following:
Various hydrogels are best suited for different types of sensing (ECG/EKG) and/or stimulations.
How much adhesion strength is provided by the hydrogel? Will supplemental medical adhesives (non-conductive) be required to effectively affix the sensor to the human?
Does the application of the sensor require the gel to allow for multiple placements?
For some applications, the FDA may require that the manufacturing facility applying the hydrogel possess bio-burden monitoring capabilities. For some facilities, this can represent a significant increase in manufacturing costs.
Attaching Medical Sensors to Humans
A critical consideration in medical sensor design is how the sensor will be attached to the human. In nearly all cases this is done via medical adhesives. More specifically, the use of medical pressure-sensitive adhesives (MPSA) are used extensively in medical sensor applications. Utilizing the proper adhesive is paramount in the success of the medical device. The following list describes areas of consideration when dealing with human skin and disposable medical sensor adhesion.
Human skin often contains water, salt, oil, cream, lotion and miscellaneous loose debris. In short, the chemistry of the surface of skin is highly variable
The entire epidermis (uppermost layer of skin) rejuvenates every 45-75 days and the very top portion of the epidermis ‘sloughs’ off every 14 days. This ever-changing environment provides a unique environment for pressure-sensitive adhesives.
A magnified view of the surface reveals the fact that skin contains a plethora of crevasses, creases, pores and hairs. Moreover, as humans age, there skin gets rougher by nearly 3-fold.
The fact that skin is designed to move as our bodies move provides yet another challenge.
Because skin is a living organ, concerns over possible allergic reactions need to be considered.
The human skin has a low surface energy.
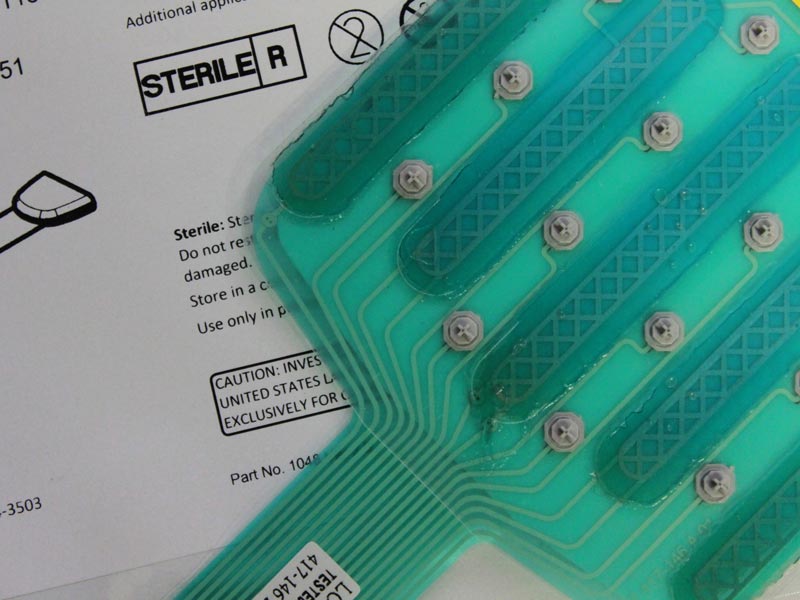
Disposable Medical Sensors: The Applications are Nearly Endless
During patient monitoring and other medical applications, there’s no room for error and no time for failure. With over 30 years’ experience in our field, we produce some of the most dependable disposable flexible medical circuits on the market. Our disposable medical sensors are regularly utilized in the following applications:
- ECG monitoring
- Cardiac analytics
- Prenatal monitoring
- Muscular assessment
- Neuromonitoring
- EEG monitoring
- Concussion diagnostics
Why Medical Device Manufacturers Choose SSI’s Products
While reliability is critical for disposable medical sensors and medical circuits, there is more and more pressure on medical device OEMs to provide economical solutions. SSI has developed processes and materials that enable us to deliver high-quality, low-cost interface products for disposable medical devices.
The truth is, medical device manufacturers have higher expectations of their suppliers. Like all health service industries, it is critical that suppliers in this market are prepared to support their customers from a quality regulatory standpoint. Whether it’s providing traceability for our products or helping customers mitigate the risks associated with using our products, SSI has extensive experience in supporting our customers’ quality and regulatory needs.
The disposable medical products market is one of the fastest growing product development fields in the U.S. economy. SSI has over 15 years of experience in this unique, dynamic field, and we’ve supplied affordable interface solutions for a broad range of disposable medical devices.
Contact SSI Electronics Today
Contact us for more information on our disposable medical sensors and other disposable medical devices, you can call 800-866-8510 or request a quote today.
